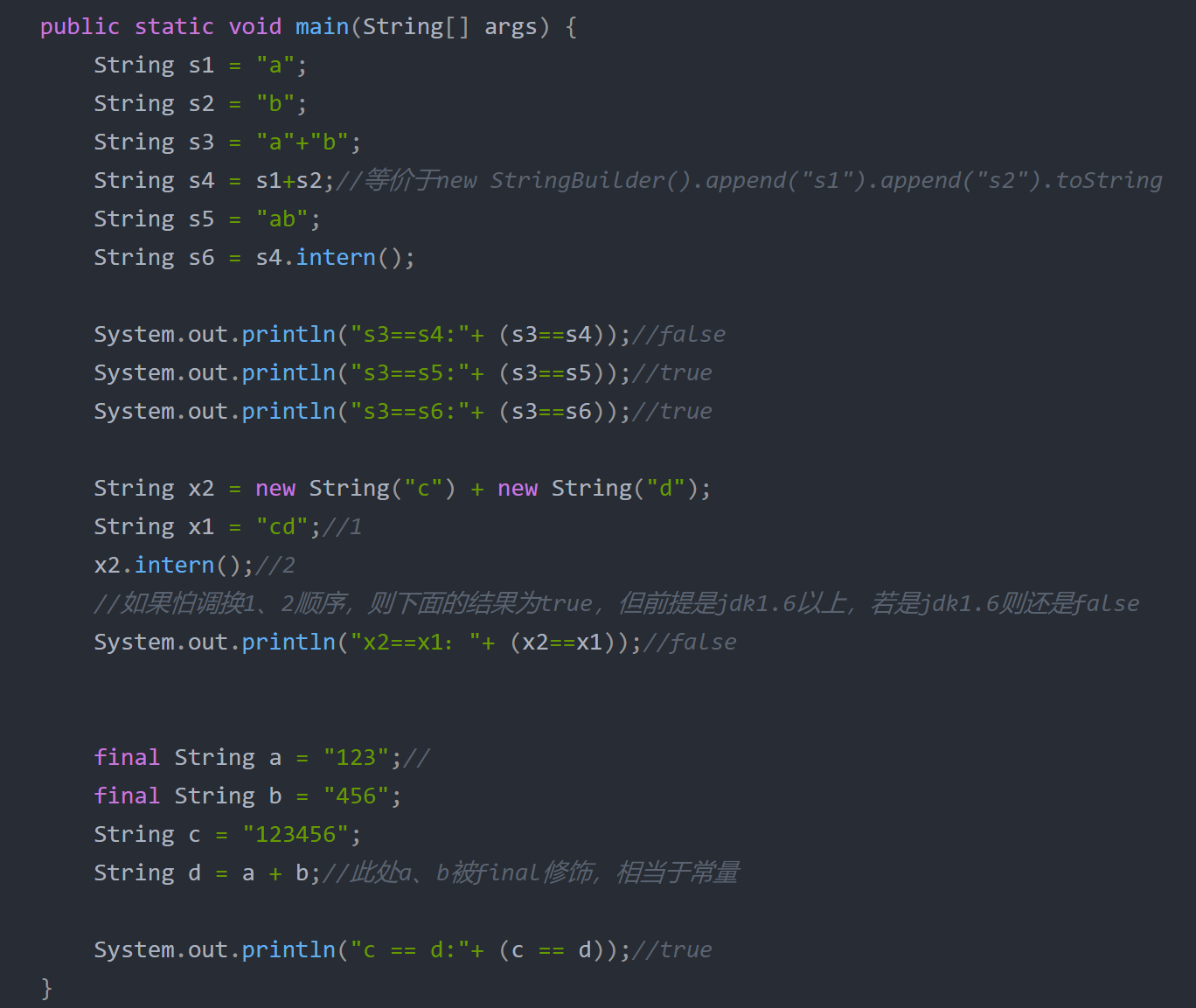
字符串常量与字符串对象
- 所有直接”abc”字面量出现的字符串,都会直接判定并进入常量池。
- new String(),一定会创建一个字符串对象,位于堆,如果没有被引用,很快会被GC
- 字符串拼接: ① 纯字符串常量相加,”hello” + “world”,编译时,String在底层会创建StringBuilder来append,但最后不会返回StingBuilder.toString()对应的String对象,而是将相加结果作为新的字符串常量存储在常量池 ② 非纯字符串常量相加,new String(“hello”) + new String(“world”); • 字符串常量池与堆中,同时创建”hello”,new String(“hello”); • 加法会暗中new StringBuilder(),然后常量池与堆中同时创建world • StringBuilder.append(),然后调用toString(),实现上会new String(“HellowWorld”),但这个字符串不会在常量池中创建!
字符串拼接原理
字符串常量的拼接原理是编译器优化,直接把常量拼接起来;字符串变量的拼接原理是StringBuilder
注意点
- 被final修饰的字符串变量,相当于常量!
- 在JDK1.7之后,intern方法,如果是第一次出现的字符串,会把现有字符串的引用放入常量池并返回!
一图解惑
后记:参考资料(常查常看) https://tech.meituan.com/2014/03/06/in-depth-understanding-string-intern.html
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903741032759310
https://www.zhihu.com/question/55994121